W3cubDocs
/scikit-learnsklearn.cluster.AffinityPropagation
-
class sklearn.cluster.AffinityPropagation(damping=0.5, max_iter=200, convergence_iter=15, copy=True, preference=None, affinity='euclidean', verbose=False)[source] -
Perform Affinity Propagation Clustering of data.
Read more in the User Guide.
Parameters: damping : float, optional, default: 0.5
Damping factor between 0.5 and 1.
convergence_iter : int, optional, default: 15
Number of iterations with no change in the number of estimated clusters that stops the convergence.
max_iter : int, optional, default: 200
Maximum number of iterations.
copy : boolean, optional, default: True
Make a copy of input data.
preference : array-like, shape (n_samples,) or float, optional
Preferences for each point - points with larger values of preferences are more likely to be chosen as exemplars. The number of exemplars, ie of clusters, is influenced by the input preferences value. If the preferences are not passed as arguments, they will be set to the median of the input similarities.
affinity : string, optional, default=``euclidean``
Which affinity to use. At the moment
precomputedandeuclideanare supported.euclideanuses the negative squared euclidean distance between points.verbose : boolean, optional, default: False
Whether to be verbose.
Attributes: cluster_centers_indices_ : array, shape (n_clusters,)
Indices of cluster centers
cluster_centers_ : array, shape (n_clusters, n_features)
Cluster centers (if affinity !=
precomputed).labels_ : array, shape (n_samples,)
Labels of each point
affinity_matrix_ : array, shape (n_samples, n_samples)
Stores the affinity matrix used in
fit.n_iter_ : int
Number of iterations taken to converge.
Notes
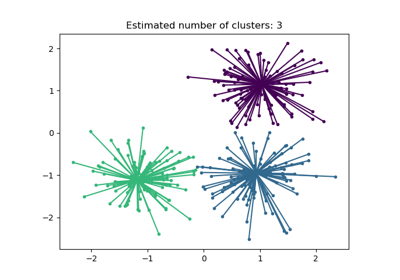
See examples/cluster/plot_affinity_propagation.py for an example.
The algorithmic complexity of affinity propagation is quadratic in the number of points.
References
Brendan J. Frey and Delbert Dueck, “Clustering by Passing Messages Between Data Points”, Science Feb. 2007
Methods
fit(X[, y])Create affinity matrix from negative euclidean distances, then apply affinity propagation clustering. fit_predict(X[, y])Performs clustering on X and returns cluster labels. get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator. predict(X)Predict the closest cluster each sample in X belongs to. set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator. -
__init__(damping=0.5, max_iter=200, convergence_iter=15, copy=True, preference=None, affinity='euclidean', verbose=False)[source]
-
fit(X, y=None)[source] -
Create affinity matrix from negative euclidean distances, then apply affinity propagation clustering.
Parameters: X: array-like, shape (n_samples, n_features) or (n_samples, n_samples) :
Data matrix or, if affinity is
precomputed, matrix of similarities / affinities.
-
fit_predict(X, y=None)[source] -
Performs clustering on X and returns cluster labels.
Parameters: X : ndarray, shape (n_samples, n_features)
Input data.
Returns: y : ndarray, shape (n_samples,)
cluster labels
-
get_params(deep=True)[source] -
Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: deep: boolean, optional :
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
Returns: params : mapping of string to any
Parameter names mapped to their values.
-
predict(X)[source] -
Predict the closest cluster each sample in X belongs to.
Parameters: X : {array-like, sparse matrix}, shape (n_samples, n_features)
New data to predict.
Returns: labels : array, shape (n_samples,)
Index of the cluster each sample belongs to.
-
set_params(**params)[source] -
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The latter have parameters of the form
<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.Returns: self :
-
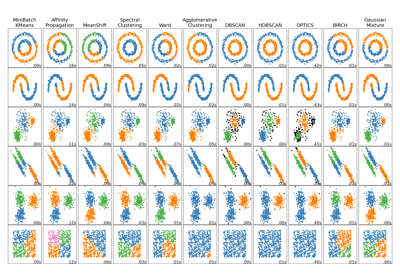
Examples using sklearn.cluster.AffinityPropagation
© 2007–2016 The scikit-learn developers
Licensed under the 3-clause BSD License.
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.cluster.AffinityPropagation.html