W3cubDocs
/scikit-learnLabel Propagation digits: Demonstrating performance
This example demonstrates the power of semisupervised learning by training a Label Spreading model to classify handwritten digits with sets of very few labels.
The handwritten digit dataset has 1797 total points. The model will be trained using all points, but only 30 will be labeled. Results in the form of a confusion matrix and a series of metrics over each class will be very good.
At the end, the top 10 most uncertain predictions will be shown.
print(__doc__) # Authors: Clay Woolam <[email protected]> # License: BSD import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import stats from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.semi_supervised import label_propagation from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report digits = datasets.load_digits() rng = np.random.RandomState(0) indices = np.arange(len(digits.data)) rng.shuffle(indices) X = digits.data[indices[:330]] y = digits.target[indices[:330]] images = digits.images[indices[:330]] n_total_samples = len(y) n_labeled_points = 30 indices = np.arange(n_total_samples) unlabeled_set = indices[n_labeled_points:] # shuffle everything around y_train = np.copy(y) y_train[unlabeled_set] = -1
Learn with LabelSpreading
lp_model = label_propagation.LabelSpreading(gamma=0.25, max_iter=5)
lp_model.fit(X, y_train)
predicted_labels = lp_model.transduction_[unlabeled_set]
true_labels = y[unlabeled_set]
cm = confusion_matrix(true_labels, predicted_labels, labels=lp_model.classes_)
print("Label Spreading model: %d labeled & %d unlabeled points (%d total)" %
(n_labeled_points, n_total_samples - n_labeled_points, n_total_samples))
print(classification_report(true_labels, predicted_labels))
print("Confusion matrix")
print(cm)
# calculate uncertainty values for each transduced distribution
pred_entropies = stats.distributions.entropy(lp_model.label_distributions_.T)
# pick the top 10 most uncertain labels
uncertainty_index = np.argsort(pred_entropies)[-10:]
Out:
Label Spreading model: 30 labeled & 300 unlabeled points (330 total)
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 1.00 1.00 23
1 0.58 0.54 0.56 28
2 0.96 0.93 0.95 29
3 0.00 0.00 0.00 28
4 0.91 0.80 0.85 25
5 0.96 0.79 0.87 33
6 0.97 0.97 0.97 36
7 0.89 1.00 0.94 34
8 0.48 0.83 0.61 29
9 0.54 0.77 0.64 35
avg / total 0.73 0.77 0.74 300
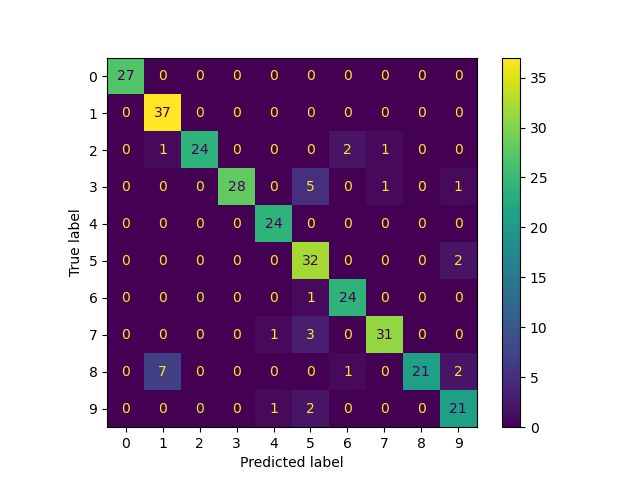
Confusion matrix
[[23 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 15 1 0 0 1 0 11 0]
[ 0 0 27 0 0 0 2 0 0]
[ 0 5 0 20 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 26 0 0 1 6]
[ 0 1 0 0 0 35 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 34 0 0]
[ 0 5 0 0 0 0 0 24 0]
[ 0 0 0 2 1 0 2 3 27]]
plot
f = plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))
for index, image_index in enumerate(uncertainty_index):
image = images[image_index]
sub = f.add_subplot(2, 5, index + 1)
sub.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
sub.set_title('predict: %i\ntrue: %i' % (
lp_model.transduction_[image_index], y[image_index]))
f.suptitle('Learning with small amount of labeled data')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.692 seconds)
Download Python source code:
plot_label_propagation_digits.py
Download IPython notebook:
plot_label_propagation_digits.ipynb
© 2007–2016 The scikit-learn developers
Licensed under the 3-clause BSD License.
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/semi_supervised/plot_label_propagation_digits.html