W3cubDocs
/scikit-learnIsotonic Regression
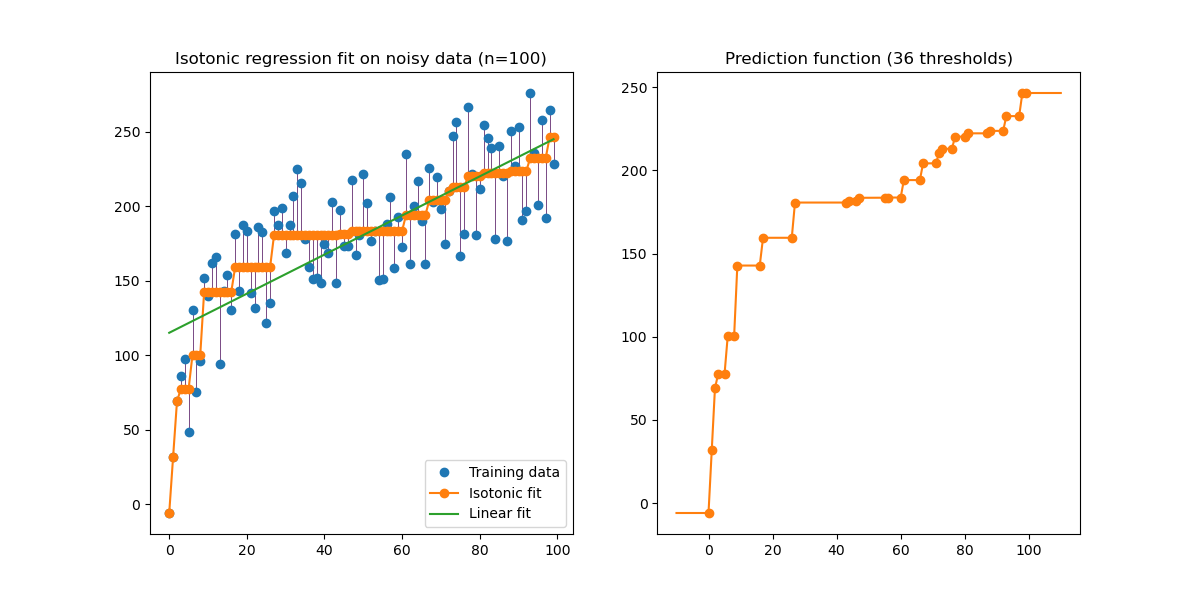
An illustration of the isotonic regression on generated data. The isotonic regression finds a non-decreasing approximation of a function while minimizing the mean squared error on the training data. The benefit of such a model is that it does not assume any form for the target function such as linearity. For comparison a linear regression is also presented.
print(__doc__) # Author: Nelle Varoquaux <[email protected]> # Alexandre Gramfort <[email protected]> # License: BSD import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.collections import LineCollection from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression from sklearn.isotonic import IsotonicRegression from sklearn.utils import check_random_state n = 100 x = np.arange(n) rs = check_random_state(0) y = rs.randint(-50, 50, size=(n,)) + 50. * np.log(1 + np.arange(n))
Fit IsotonicRegression and LinearRegression models
ir = IsotonicRegression() y_ = ir.fit_transform(x, y) lr = LinearRegression() lr.fit(x[:, np.newaxis], y) # x needs to be 2d for LinearRegression
plot result
segments = [[[i, y[i]], [i, y_[i]]] for i in range(n)]
lc = LineCollection(segments, zorder=0)
lc.set_array(np.ones(len(y)))
lc.set_linewidths(0.5 * np.ones(n))
fig = plt.figure()
plt.plot(x, y, 'r.', markersize=12)
plt.plot(x, y_, 'g.-', markersize=12)
plt.plot(x, lr.predict(x[:, np.newaxis]), 'b-')
plt.gca().add_collection(lc)
plt.legend(('Data', 'Isotonic Fit', 'Linear Fit'), loc='lower right')
plt.title('Isotonic regression')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.160 seconds)
Download Python source code:
plot_isotonic_regression.py
Download IPython notebook:
plot_isotonic_regression.ipynb
© 2007–2016 The scikit-learn developers
Licensed under the 3-clause BSD License.
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/plot_isotonic_regression.html