W3cubDocs
/scikit-learnNearest Neighbors regression
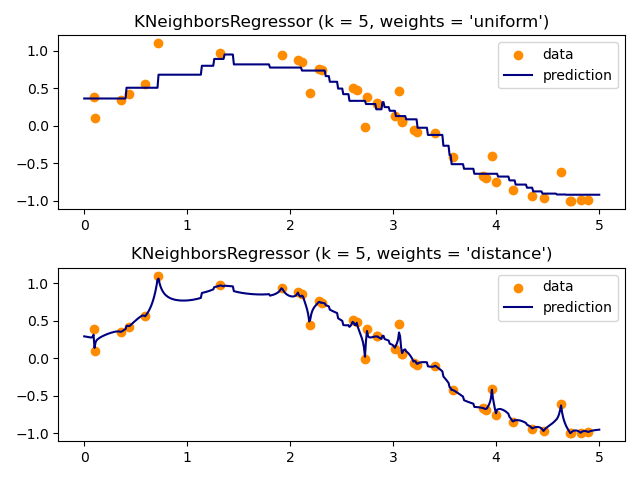
Demonstrate the resolution of a regression problem using a k-Nearest Neighbor and the interpolation of the target using both barycenter and constant weights.
print(__doc__) # Author: Alexandre Gramfort <[email protected]> # Fabian Pedregosa <[email protected]> # # License: BSD 3 clause (C) INRIA
Generate sample data
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import neighbors np.random.seed(0) X = np.sort(5 * np.random.rand(40, 1), axis=0) T = np.linspace(0, 5, 500)[:, np.newaxis] y = np.sin(X).ravel() # Add noise to targets y[::5] += 1 * (0.5 - np.random.rand(8))
Fit regression model
n_neighbors = 5
for i, weights in enumerate(['uniform', 'distance']):
knn = neighbors.KNeighborsRegressor(n_neighbors, weights=weights)
y_ = knn.fit(X, y).predict(T)
plt.subplot(2, 1, i + 1)
plt.scatter(X, y, c='k', label='data')
plt.plot(T, y_, c='g', label='prediction')
plt.axis('tight')
plt.legend()
plt.title("KNeighborsRegressor (k = %i, weights = '%s')" % (n_neighbors,
weights))
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.118 seconds)
Download Python source code:
plot_regression.py
Download IPython notebook:
plot_regression.ipynb
© 2007–2016 The scikit-learn developers
Licensed under the 3-clause BSD License.
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/neighbors/plot_regression.html